Exploring Sustainable Practices in Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry, a cornerstone of modern life, faces increasing scrutiny regarding its environmental footprint. From the extraction of raw materials to the disposal of finished products, every stage of an electronic device's lifecycle carries implications for the planet. As global demand for digital devices and advanced technology continues to grow, there is a crucial need to adopt and scale sustainable practices across the entire manufacturing process. This article delves into the various strategies and innovations being implemented to make electronics production more environmentally responsible, addressing challenges in areas such as resource consumption, energy use, and waste generation.
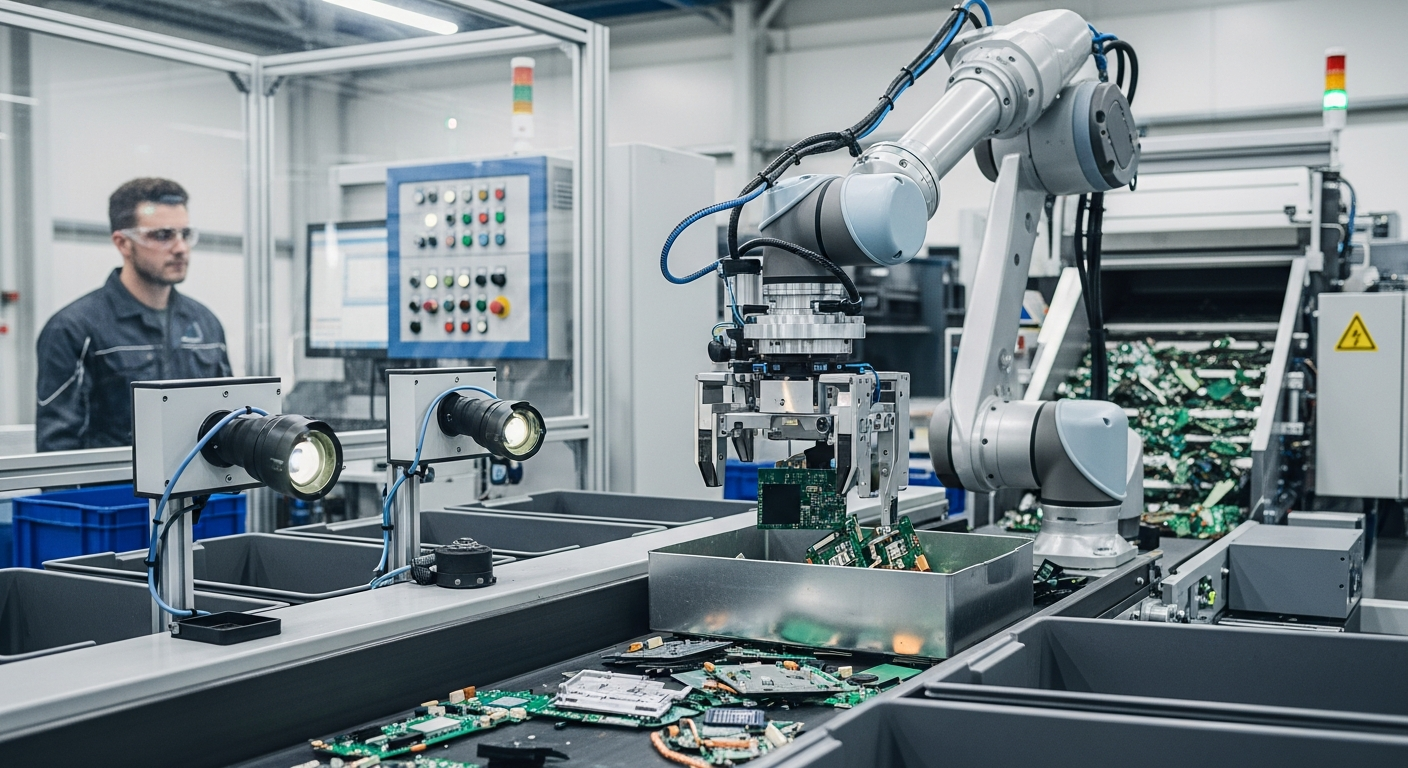
Sustainable Material Sourcing for Semiconductors and Displays
Sustainable electronics manufacturing begins with responsible material sourcing, particularly for critical components like semiconductors and displays. The extraction of raw materials such as rare earth elements, copper, and tin can lead to significant environmental degradation and social issues. Manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to ethical mining practices, minimize ecological damage, and ensure fair labor conditions. Furthermore, there are growing efforts to incorporate recycled content into new products, reducing the demand for virgin materials. Innovations are also exploring alternative, more abundant, or even bio-based materials to replace traditionally resource-intensive components, aiming for a more circular material flow within the industry and reducing reliance on finite resources.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency in Processor and Hardware Production
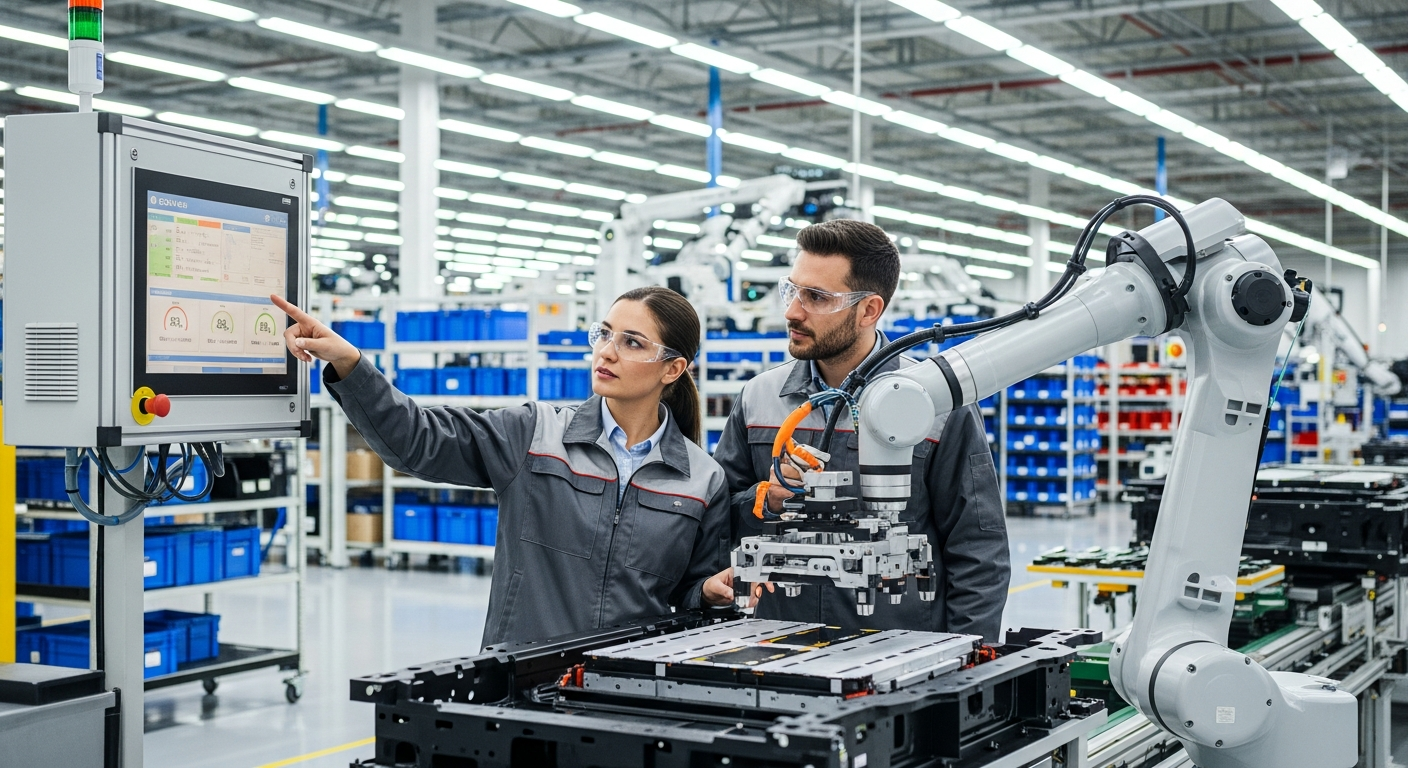
The fabrication of complex components like processors and other integral hardware is inherently energy-intensive. Semiconductor foundries, for instance, operate sophisticated machinery within highly controlled cleanroom environments, demanding substantial electricity consumption. To address this, manufacturers are investing in advanced energy management systems, optimizing production processes, and upgrading to more energy-efficient equipment. The integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, directly into manufacturing facilities or through power purchase agreements, is also gaining traction. These initiatives not only reduce the carbon footprint but can also lead to operational cost savings, demonstrating that environmental responsibility can align with economic viability and improve overall operational efficiency.
Designing for Longevity and Recyclability in Gadgets
A significant challenge in electronics sustainability is the short lifespan of many consumer gadgets, leading to substantial electronic waste. Sustainable design principles advocate for creating hardware that is durable, repairable, and upgradable, thereby extending product life cycles. This includes designing components, such as those within displays, to be easily replaceable rather than necessitating the disposal of an entire device. Modular designs, for example, allow users or repair centers to swap out faulty parts. Furthermore, designing for ease of disassembly is crucial for efficient recycling, enabling the recovery of valuable materials like precious metals and rare earths. Such design choices are fundamental to transitioning towards a more circular economy where resources are kept in use for longer, reducing the need for new raw material extraction.
Innovations in Sustainable Technology and Digital Manufacturing
The broader spectrum of technology and digital manufacturing is seeing continuous innovation aimed at reducing environmental impact. This includes the development of more efficient manufacturing processes that minimize waste, such as precision manufacturing techniques that reduce material offcuts for small components. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) offers another avenue for sustainability by creating complex parts with minimal material waste and enabling on-demand production. Beyond the factory floor, advancements in digital supply chain management leverage connectivity and data analytics to optimize logistics, reduce transportation emissions, and improve inventory management, further enhancing overall operational efficiency. These technological advancements contribute to a more streamlined and environmentally conscious production model for all types of hardware.
The Role of Sensors and Connectivity in Process Optimization
Integrated sensors and advanced connectivity play a pivotal role in optimizing manufacturing processes for greater sustainability. By deploying sensors throughout production lines, manufacturers can gather real-time data on critical parameters such as energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation. This digital intelligence allows for immediate identification of inefficiencies and prompt corrective actions, leading to significant resource savings. For example, intelligent systems can adjust machinery operation based on demand, preventing unnecessary power usage. The insights gained from these connected systems enable continuous improvement in manufacturing processes, driving down environmental impact and improving resource efficiency across the production of various electronic components, from processors to displays.
Key Organizations and Initiatives Promoting Sustainable Electronics
Various organizations and industry initiatives are actively working to promote and implement sustainable practices within the electronics manufacturing sector. These efforts often focus on setting standards, certifying products, and fostering collaboration across the supply chain to drive environmental improvements.
| Organization/Initiative | Focus Areas | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| EPEAT (Electronic Product Environmental Assessment Tool) | Product environmental performance | Global ecolabel for electronics, helping purchasers identify greener products based on criteria for design, energy, and end-of-life management. |
| Responsible Business Alliance (RBA) | Supply chain sustainability | Sets standards for labor, health & safety, environment, ethics, and management systems in electronics supply chains. |
| Conflict-Free Sourcing Initiative (CFSI) | Mineral sourcing ethics | Provides tools and resources for companies to make responsible sourcing decisions regarding conflict minerals (tin, tantalum, tungsten, gold). |
| Green Electronics Council (GEC) | Advancing sustainable electronics | Manages the EPEAT registry, drives innovation, and promotes education on sustainable electronics. |
| European Union WEEE Directive | E-waste management and recycling | Mandates the collection, treatment, and recycling of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) across EU member states. |
| Cradle to Cradle Products Innovation Institute | Circular design | Certifies products based on material health, material reutilization, renewable energy, water stewardship, and social fairness. |
| Ellen MacArthur Foundation | Circular economy promotion | Advocates for and develops frameworks for a circular economy, including specific initiatives for electronics. |
| TCO Certified | IT product sustainability | International sustainability certification for IT products covering social and environmental criteria throughout the product life cycle. |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The drive towards sustainable practices in electronics manufacturing is a multifaceted endeavor that requires continuous innovation and commitment. From the initial responsible sourcing of materials for semiconductors and displays to the energy-efficient production of processors and hardware, every stage holds potential for improvement. Designing gadgets for longevity and recyclability, coupled with robust end-of-life management, is crucial for establishing a truly circular economy. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of digital tools and sensors will further enhance efficiency, paving the way for an electronics industry that is both innovative and environmentally conscious.





